Periodontal disease happens in four different stages. Learn about the stages of gum disease and how to deal with each of them.
Did you know that almost half of US adults aged 30 and older have periodontal (gum) disease?
Almost a quarter of these individuals already have a moderate form of the disease. Another 8.5% have severe periodontal disease.
These are the two stages of gum disease with the highest risk of bone and tooth loss.
This is why it's very important to pay attention to the signs of early gum disease. As soon as you notice these signs, you should visit a gum disease specialist in Columbia , MD. The sooner you do, the better your chances of preventing its progression.
Ready to learn more about periodontal disease stages and how to tell which one you have? Keep reading then, as that's what you'll learn in this post!
The Symptoms of Gum Disease
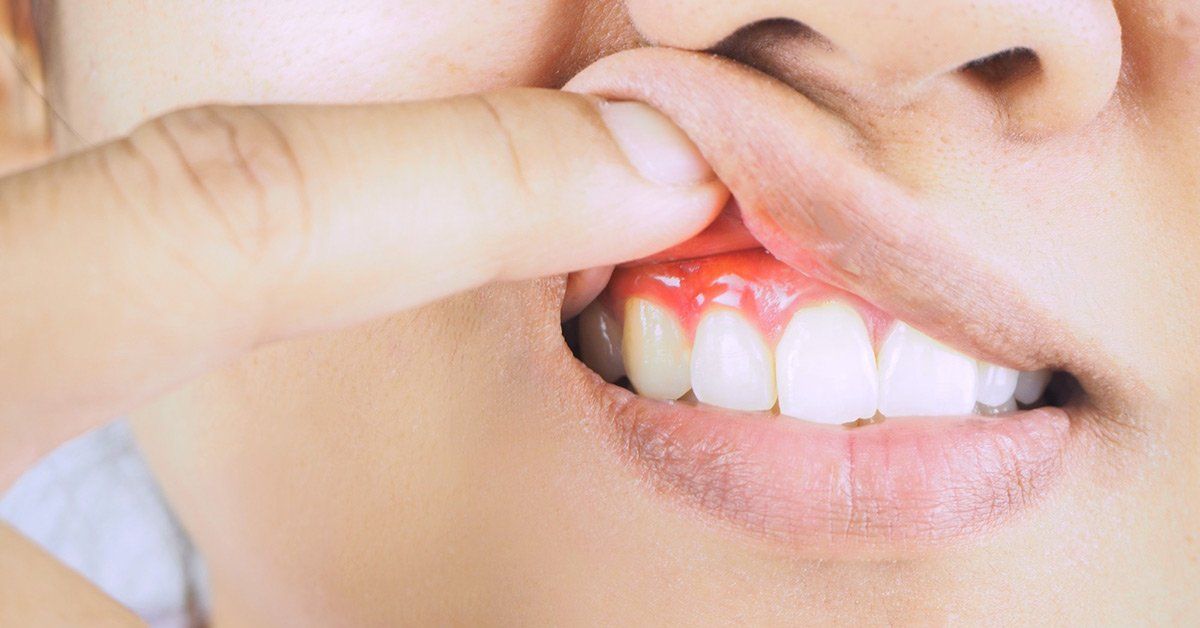
The symptoms usually vary based on the stage or severity of the periodontal disease. For example, during the initial gingivitis stages, you may only experience swollen gums. Your gums may also bleed whenever you floss or brush.
If allowed to progress, the disease can trigger more severe symptoms, including:
- halitosis or bad breath
- gum recession
- hardened plaque (tartar) on the teeth
- loose teeth
- a foul taste that doesn't disappear
Don't let gum disease progress, otherwise, you're at risk of losing your natural teeth. If you've noticed gum swelling and bleeding, it's time to see your Columbia, MD dentist. You also switch to periodontal toothpaste, which may help treat early gum disease.
Health Conditions That Periodontal Disease Can Cause
Leaving gum disease untreated can result in the loss of your permanent teeth. Without the stimulation that the teeth provide, the jawbone will start to resorb. Unless dental implants replace the lost teeth, more jawbone loss will occur.
Over time, the loss of bone can cause changes to the facial structure. The lips and cheeks will start to sink and look quite unpleasant.
Untreated periodontal disease can also result in the immune system becoming "hyperactive". Over time, the pathogens that cause the gum infection can spread into the bloodstream. According to scientists, this can damage the blood vessels in the heart and even the brain.
People who have gum disease are also at a higher risk of other chronic diseases. Periodontitis, for instance, can raise hypertension risks by 22% to 49%.Who Can Get Gum Disease?
People with poor dental hygiene (those who don't brush or floss at least twice a day) will get gum disease. Those who smoke are also twice as likely to develop periodontal disease than those who don't. Some medications, such as anticonvulsants and anti-anginas, can also raise gum disease risk.
What Exactly Is Periodontal Disease and What Causes It?
Periodontal or gum disease is an infection of the gums and periodontal tissues. Untreated, the infection can kill enough tissue and spread to the underlying bone.
This infection usually starts because of poor brushing and flossing habits. After all, inside the mouth are about 700 strains and species of oral bacteria. Some of these are pathogens, contributing to the formation of plaque.
Dental plaque -- the sticky, "yucky" film that forms on the surface of the teeth -- is the main cause of gum disease. If you don't remove all the plaque on your teeth, they can also invade the gums. Unremoved plaque also hardens into tartar, which can irritate and infect the gums.
Viruses, oral trauma, and some autoimmune diseases can also cause gum disease. Vitamin C deficiency also increases one's risk of developing periodontal disease.The Four Stages of Gum Disease
There are four different periodontal disease stages.
Gingivitis is the earliest stage. It can progress into the second stage called "slight periodontal disease". From here, it can become moderate periodontal disease, and ultimately, advanced periodontal disease.
Gingivitis
Of all gum disease stages, gingivitis is the easiest to treat, as it's still non-destructive. As the earliest stage, it affects only the gingiva. The gingiva is the part of the gums that surround the base of the upper and lower teeth.
Gingivitis results in the inflammation of the gingiva. At this point, it causes swollen, tender, and sore gums. It can also make the gums more prone to bleeding.
Slight Periodontal Disease
During the early gingivitis stages, gum inflammation can occur in as little as five days. Within two to three weeks, the signs of generalized gingivitis become more noticeable. If you still leave this untreated, it would progress to slight periodontal disease.
At this stage, your gums will start to pull away or "recede" from your teeth. This will then create tiny pockets between your teeth and the affected gums. More harmful bacteria can then invade these "spaces", causing even more bleeding.
Moderate Periodontal Disease
More bleeding and gum recession will occur during this third stage of gum disease. As more tissues die, your teeth will start to lose support and they will become movable. The infection can also result in a whole-body inflammatory response.
Advanced Periodontal Disease
This is the worst of the four gum disease stages, causing the most destruction in your gums and bones. The tissues that hold and connect your teeth to the bone will already deteriorate. You're likely to experience extreme pain and also have severe bad breath.
This is also the point where you're at the highest risk of losing your teeth.
Healthy Gums Are Key to Keeping Your Permanent Teeth in Place
There you have it, your complete guide to the four stages of gum disease and the havoc they can wreak to your mouth. As you can see, most cases of the disease are preventable through proper oral hygiene. However, it's not enough to just use periodontal toothpaste -- it's best to also see your dentist at least twice a year.
It's even more important to book a dental appointment as soon as you notice the early signs of gum disease. This way, you can prevent gingivitis from progressing into advanced periodontal disease. The earlier you have gum disease treated, the lower your risks of suffering from teeth loss.
If you suspect that you have gum disease, we here at Smile Savers Dentistry can help. Our dental team in Columbia, MD specializes in LANAP treatment for gum disease. Get in touch with us now so we can start the process of making your gums healthy once again!