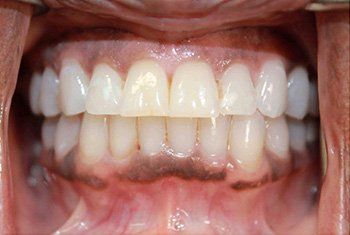
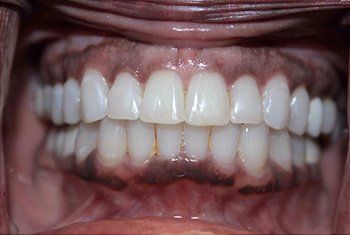
Tooth Decay In Columbia, MD
Understanding Tooth Decay - Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Smile Savers Dentistry is committed to helping patients achieve and maintain optimal dental health. Our practice, led by Dr. Anuja Patel as our head dentist, offers comprehensive dental services, including the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of decay. This guide will explore the causes, signs, and treatments of tooth decay. It will empower you to take proactive measures to protect your smile.
What is Tooth Decay?
Dental caries, or cavities, are common conditions of oral health that destroy tooth structure. This is caused by bacterial activity. The bacteria in plaque produces acids which slowly erodes the enamel of the tooth. Untreated tooth decay can cause pain, infection, and even tooth loss.
Causes of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is caused by several factors, including:
Schedule Your Family's Dental Appointment Today
Do not wait for the problem to worsen if you are experiencing tooth decay symptoms or have been overdue for a dental examination. Make an appointment with Smile Savers Dentistry to receive the individualized care and treatment that you need for your oral health and smile. Call us to schedule your appointment and begin the journey toward a happier, healthier smile.
Symptoms of Tooth Decay
Early tooth decay can be difficult to detect, so regular dental examinations are essential for early detection. However, as decay progresses, you may experience:
Tooth Sense: The enamel layer may be exposed, causing sensitivity to sweets, acidic drinks, and hot foods.
Toothache: A persistent or intermittent toothache, which can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, could indicate an infection or decay within the tooth.
Visible changes: Discoloration or dark spots on the surface of teeth can indicate decay.
Bad breath: A persistent bad smell (halitosis), can be caused by bacterial activity or decay in the mouth.
Pain While Chewing: Any discomfort or pain, particularly in certain areas of the mouth or when chewing or biting, could indicate underlying damage or decay.
Treating Tooth Decay
Treatment for tooth decay is dependent on the severity of the damage. It may include:
Fillings Dr. Patel can recommend dental fillings for small to medium cavities to restore damaged tooth structure and prevent further decay. Fillings can be made from tooth-colored composite resins or amalgam materials, and they are custom-matched so that they blend seamlessly with the natural teeth.
Dental Crowns: A dental crown is recommended when decay has caused extensive tooth damage or the structure of the teeth has been weakened. Crowns are made-to-measure caps that cover all visible portions of the teeth, restoring their strength, functionality, and appearance.
Root Canal Therapy If decay has penetrated the innermost layer (dental pulp), it can cause inflammation, infection, and severe pain. Root canal therapy involves the removal of the infected tissues, disinfecting the canal, and sealing it. This prevents further infection. This procedure can prevent the extraction of a tooth that is severely infected or decayed and maintain its function.
Tooth Extraction: If the tooth is irreparably damaged or has advanced decay, it may be necessary to extract it and avoid further complications. Dr. Patel can discuss your options for tooth replacement, including dental implants, bridges, or dentures. This will restore the function and aesthetics of your smile.
Prevention: The best way to prevent tooth decay is prevention. Dr. Patel can recommend preventive measures, such as fluoride treatments and dental sealants. He may also recommend regular dental cleanings, exams, and dental examinations to maintain your dental health and reduce decay risk.
Teeth Whitening and Tooth Colored Fillings
Used to Brighten Teeth and Remove Worn Metal Fillings
HOW TO PREVENT TOOTH DECAY
Although tooth decay is an extremely common dental issue, it can be prevented with regular dental care and good oral hygiene. Here are a few tips to prevent tooth decay.
Brushing
Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste. Use a toothbrush with a soft bristle. Brush for two minutes and make sure you cover all surfaces of your teeth, including the gumline.
Flossing
Clean between your teeth every day with dental floss or an interdental cleaner to remove plaque and food debris from areas where your toothbrush cannot reach.
Healthy Diet
Limit acidic and sugary foods and beverages and choose tooth-friendly options such as dairy products, fruits, vegetables, and water. Snacking between meals can lead to tooth decay.
Schedule Regular Dental Check-Ups
Dr. Patel will schedule regular dental cleanings every six months, or at his discretion. These visits enable early detection of decayed teeth and the professional removal of tartar and plaque.
Fluoride
Use fluoride toothpaste, mouthwash, and dental sealants as well to protect enamel from decay.
Do Not Smoke
Smoking and smokeless tobacco use increases the risk of oral cancer, tooth decay, and gum disease. You can improve both your oral and overall health by quitting tobacco use.